Scan Wrappers and Hierarchical Scan (Part 1)
DFT Basics : Article #19
In the previous 18 articles of the DFT Basics series, we explored topics such as Scan Insertion, Scan Compression, On-Chip Clock Controller, and ATPG Pattern Generation. In the upcoming posts, we will continue our discussion on ATPG concepts, including coverage analysis and improvement.
In this blog, however, let’s take a brief detour from the ATPG topic and explore the concept of Hierarchical Scan.
Let’s get Started !
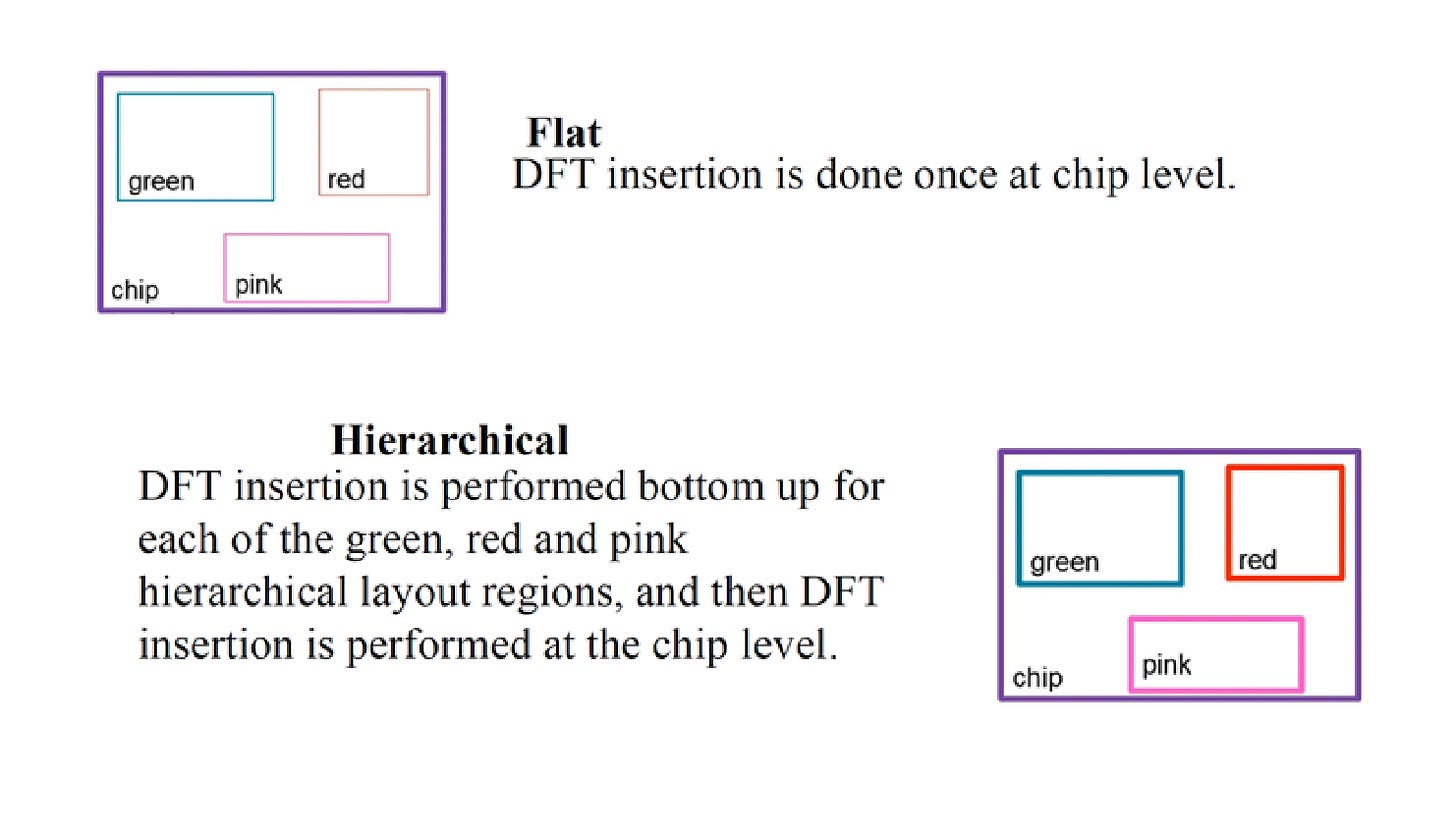
Flat Vs Hierarchical Scan
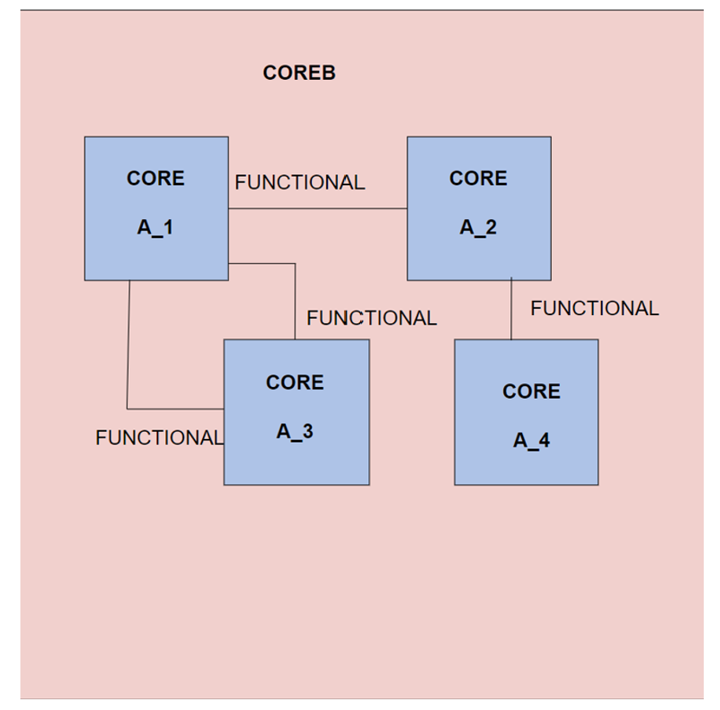
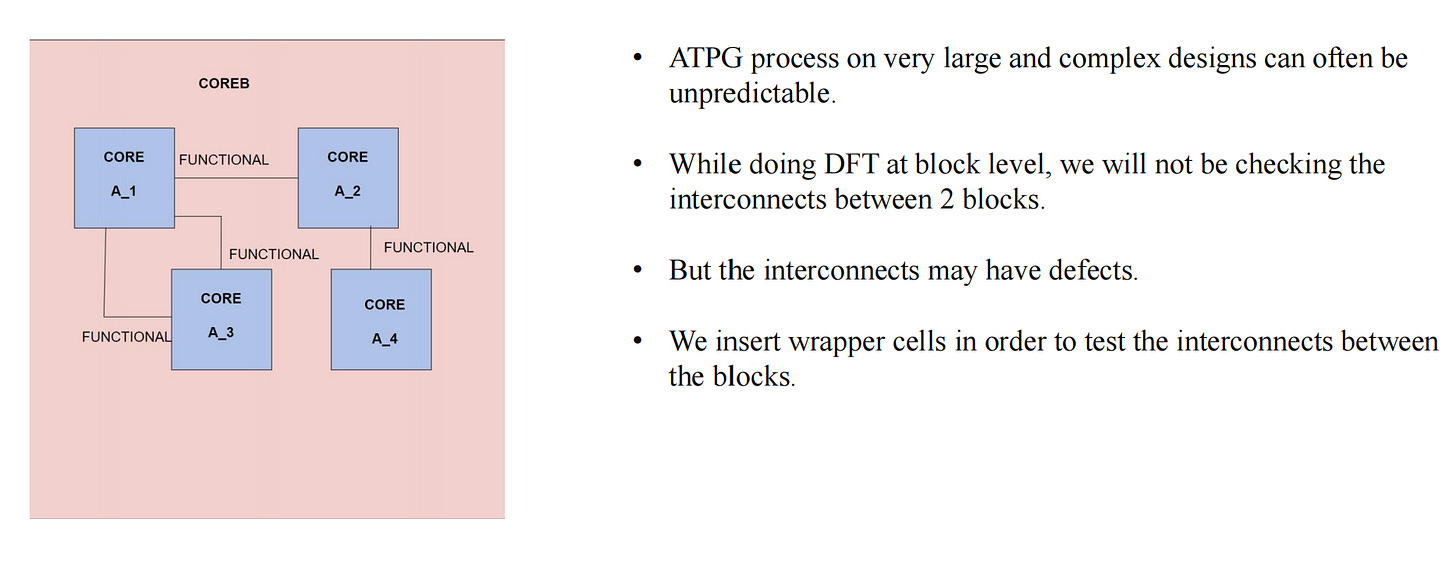
Let’s explore Hierarchical Scan concepts using the below design :
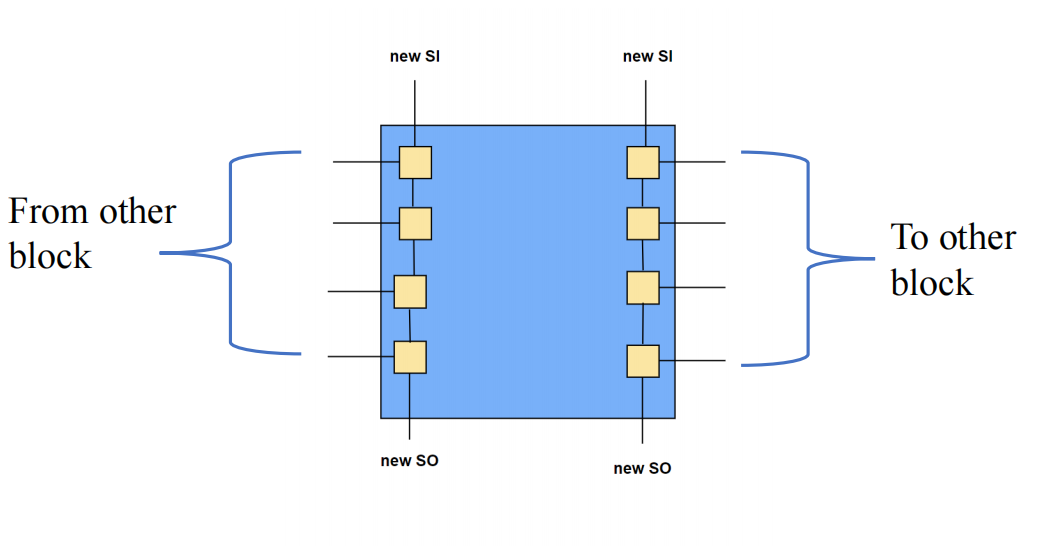
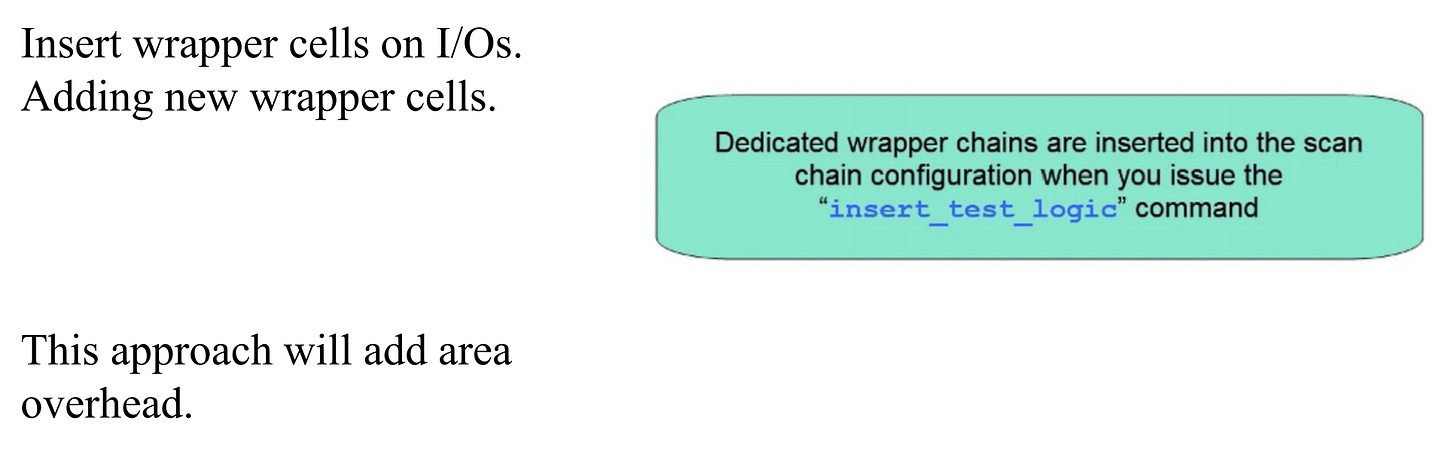
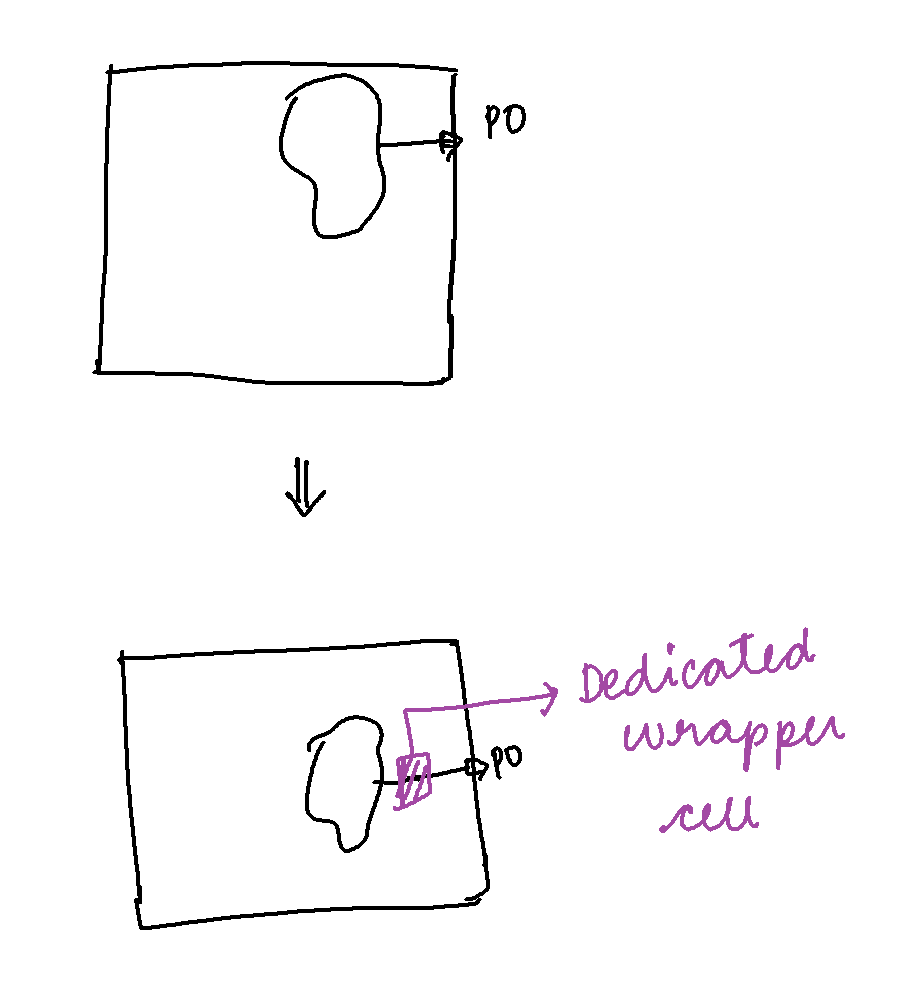
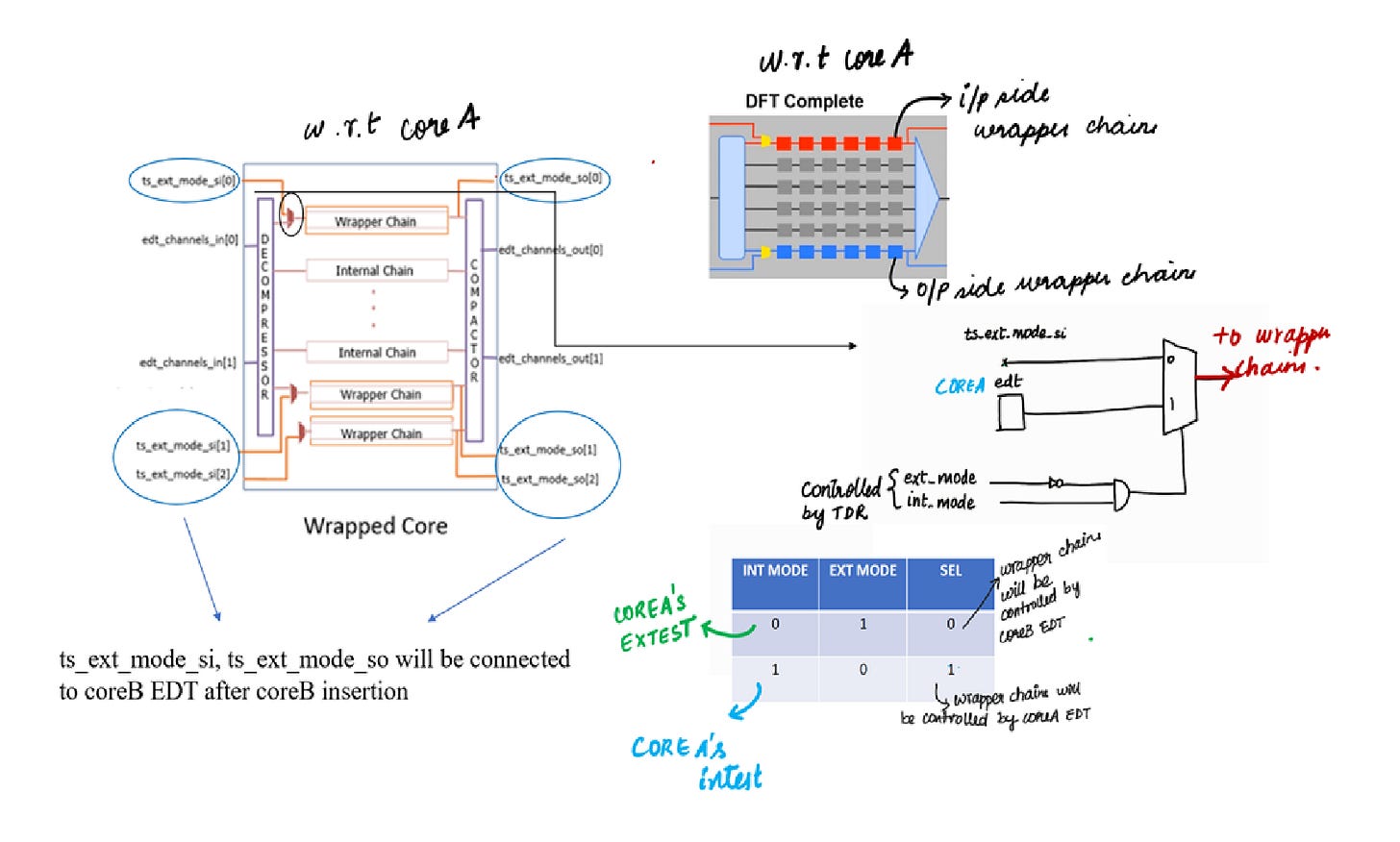
Wrapper Insertion (we will explore w.r.t CoreA level)
Wrapper Chains
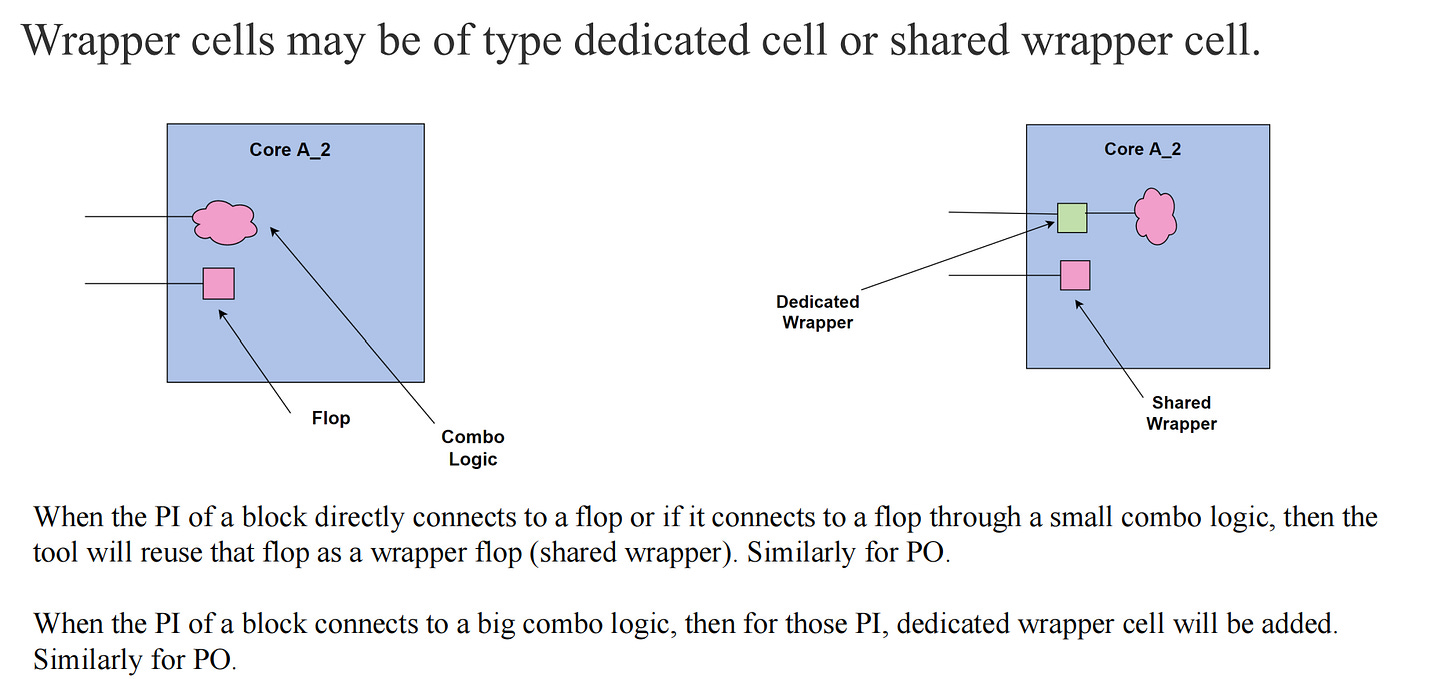
Types of Wrapper Cells
< < Note : PI stands for Primary Input (functional input) and PO stands for Primary Output (functional output)> >
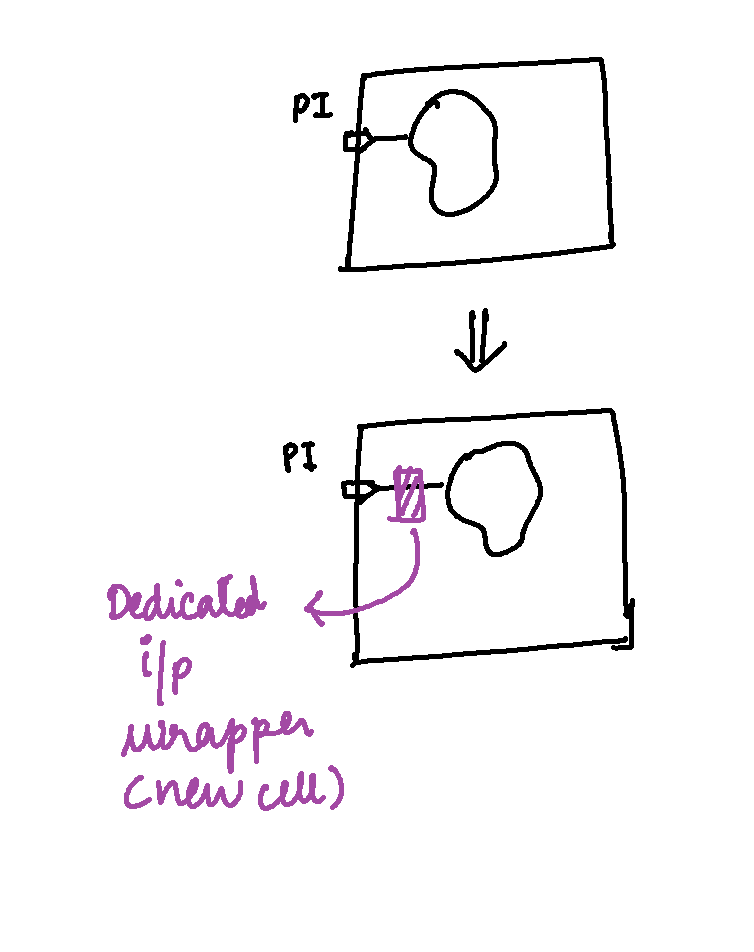
Dedicated Wrapper Cell
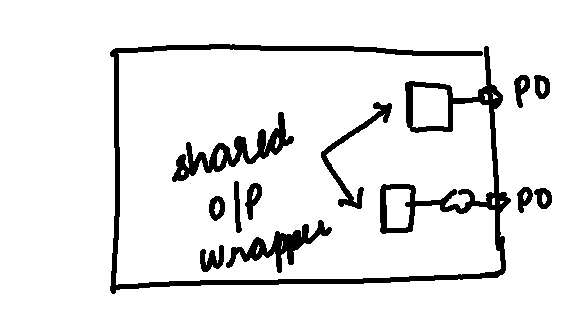
Shared Wrapper Cell
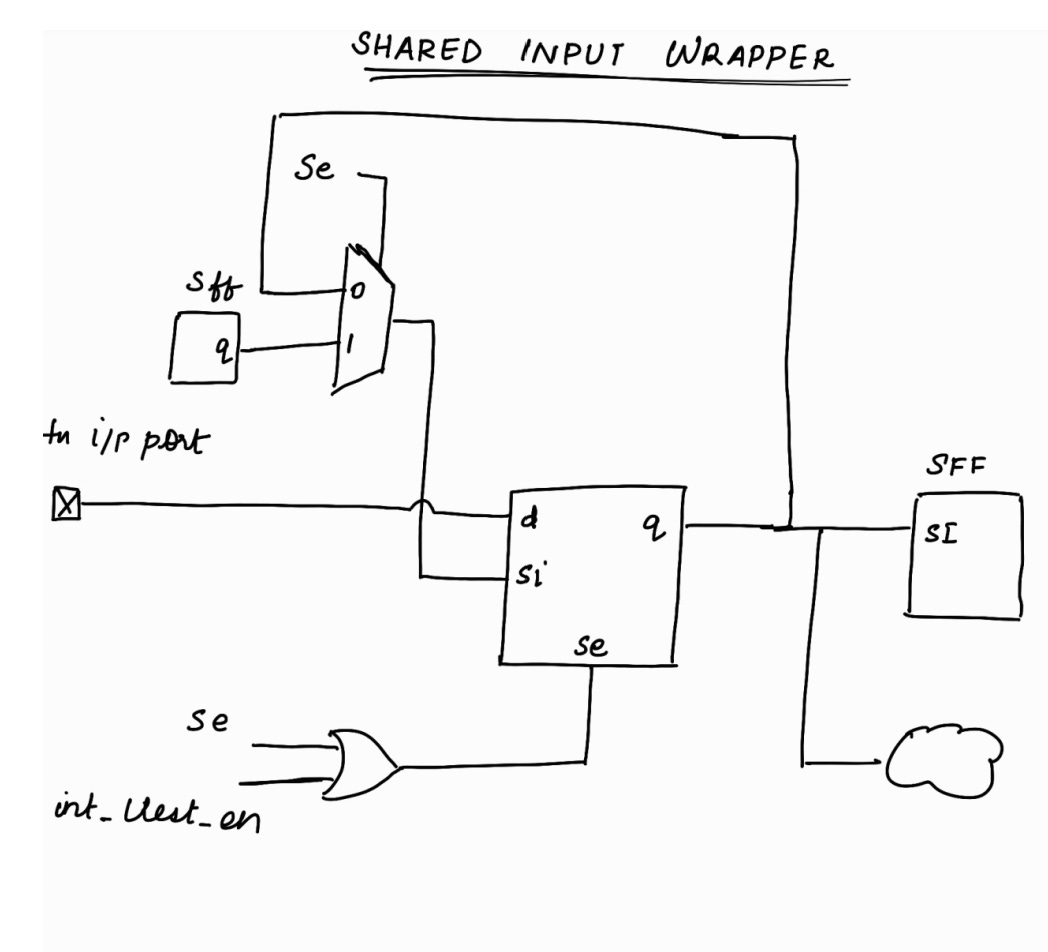
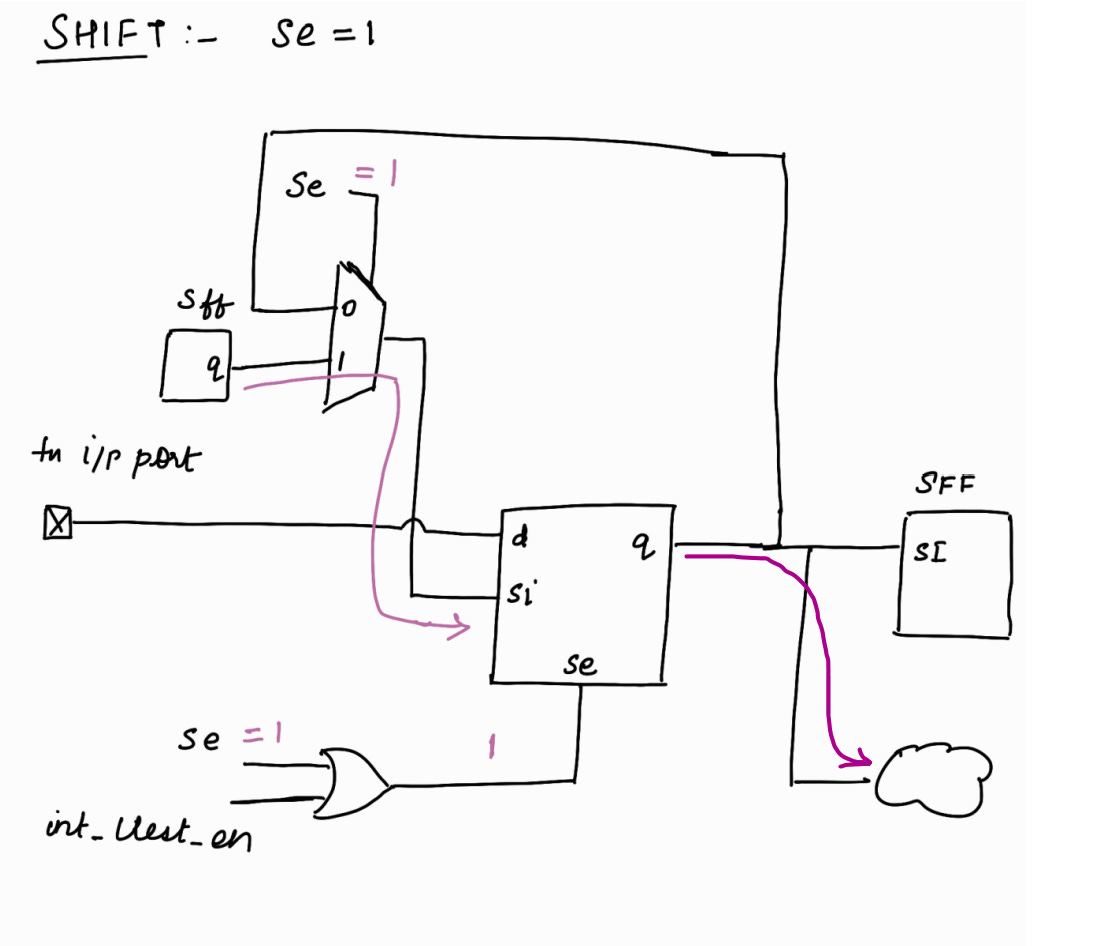
Let’s explore Shared Input Wrapper Cell !
Note :
se is Scan Enable. It will be a top level port.
int_ltest_en will be controlled by TDR
Shift Phase :
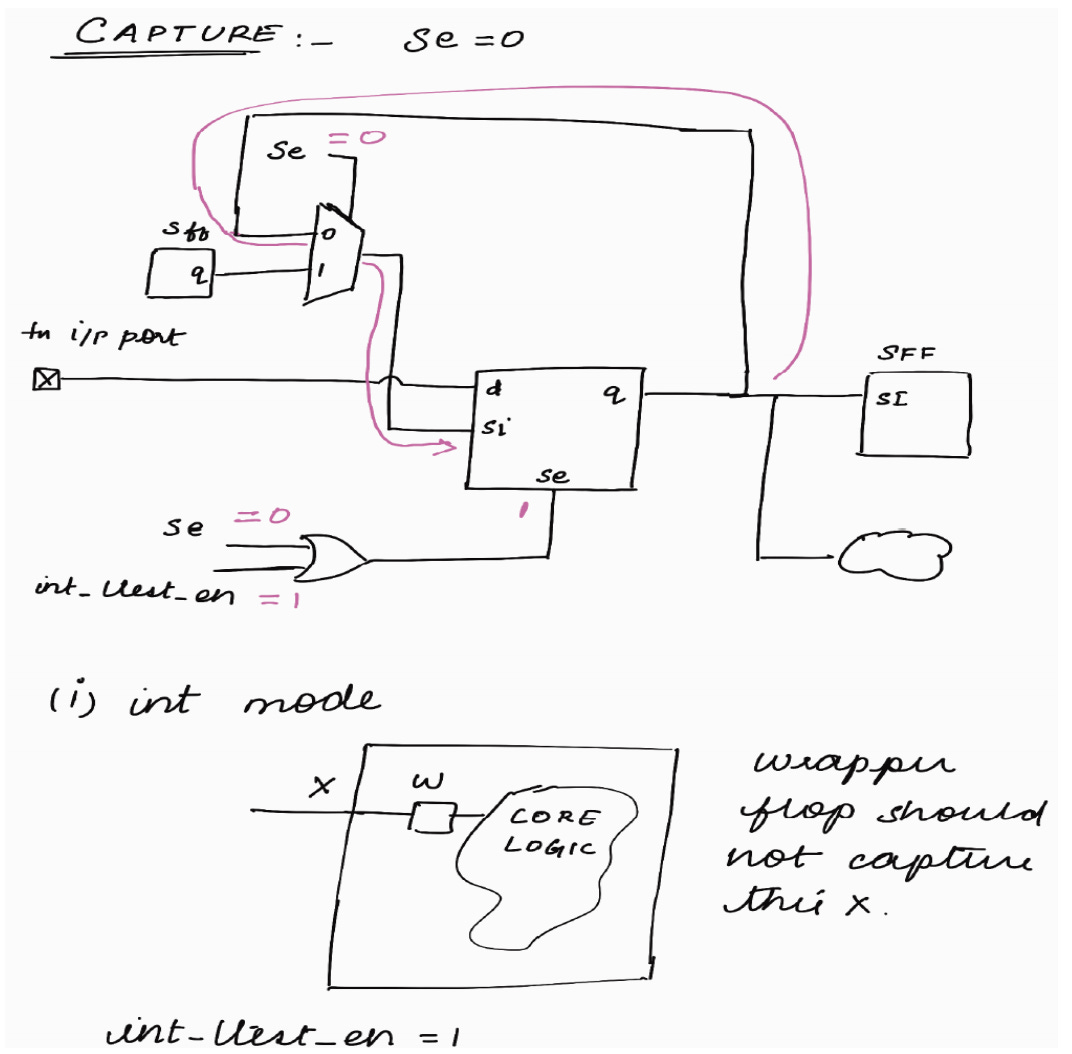
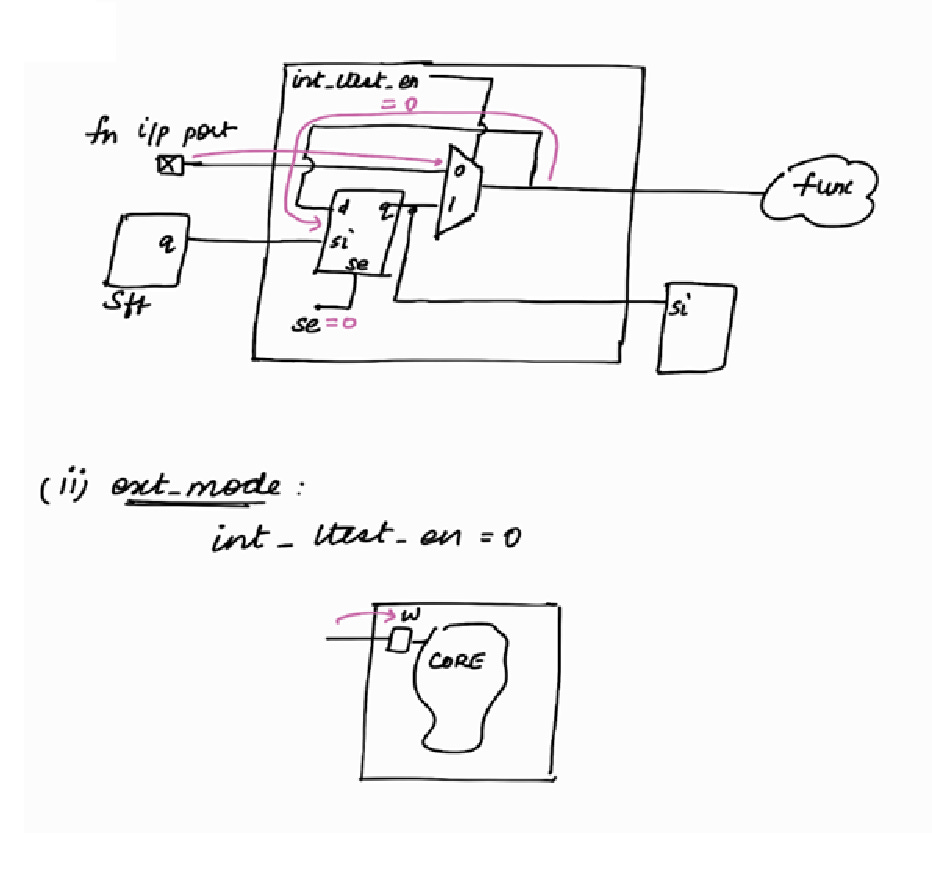
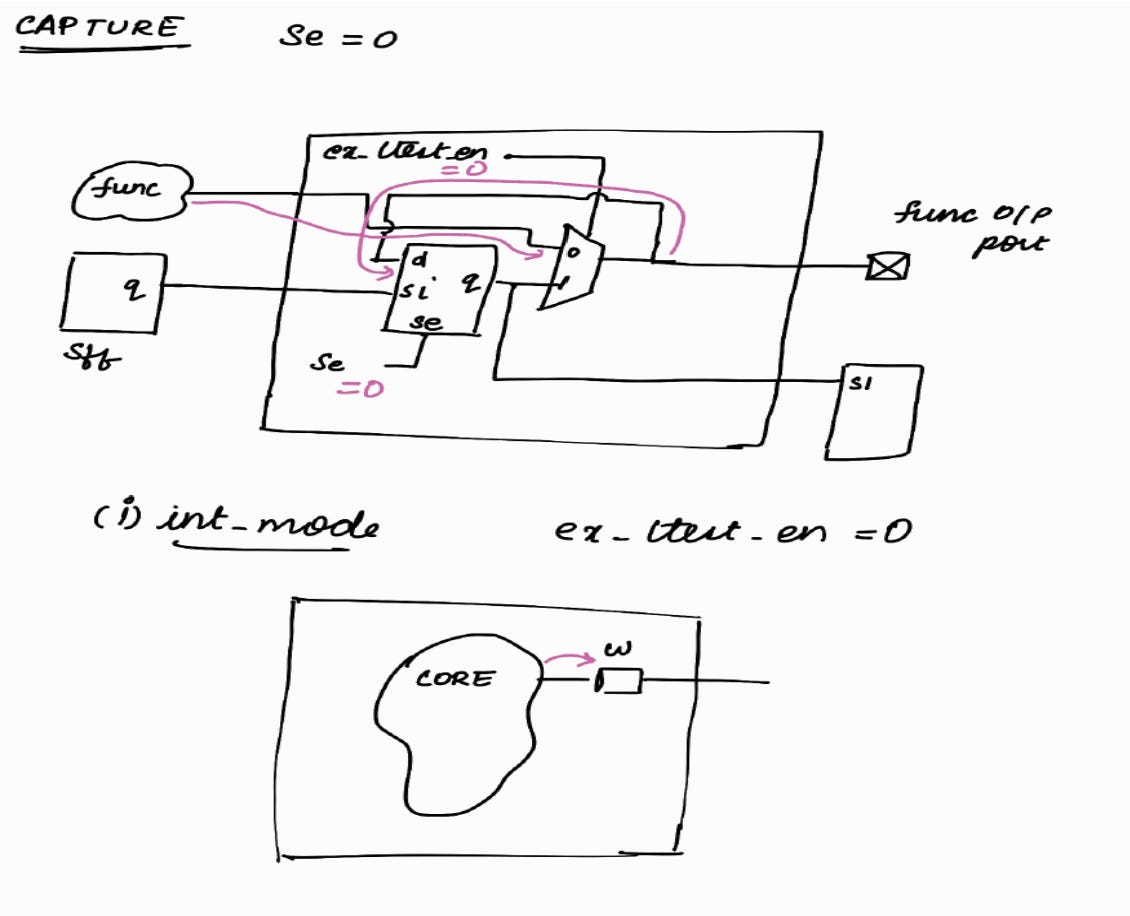
Capture Phase : (int mode)
< < In int_mode, only the logic internal to the block will be active. Logic external to the block will not be active. It will be X > >
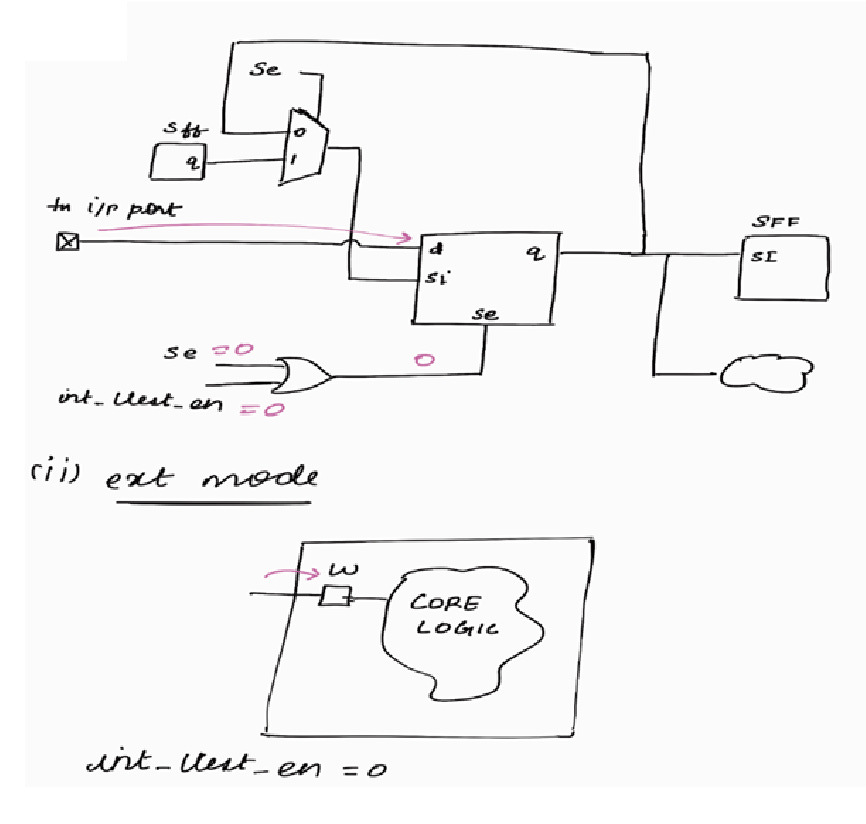
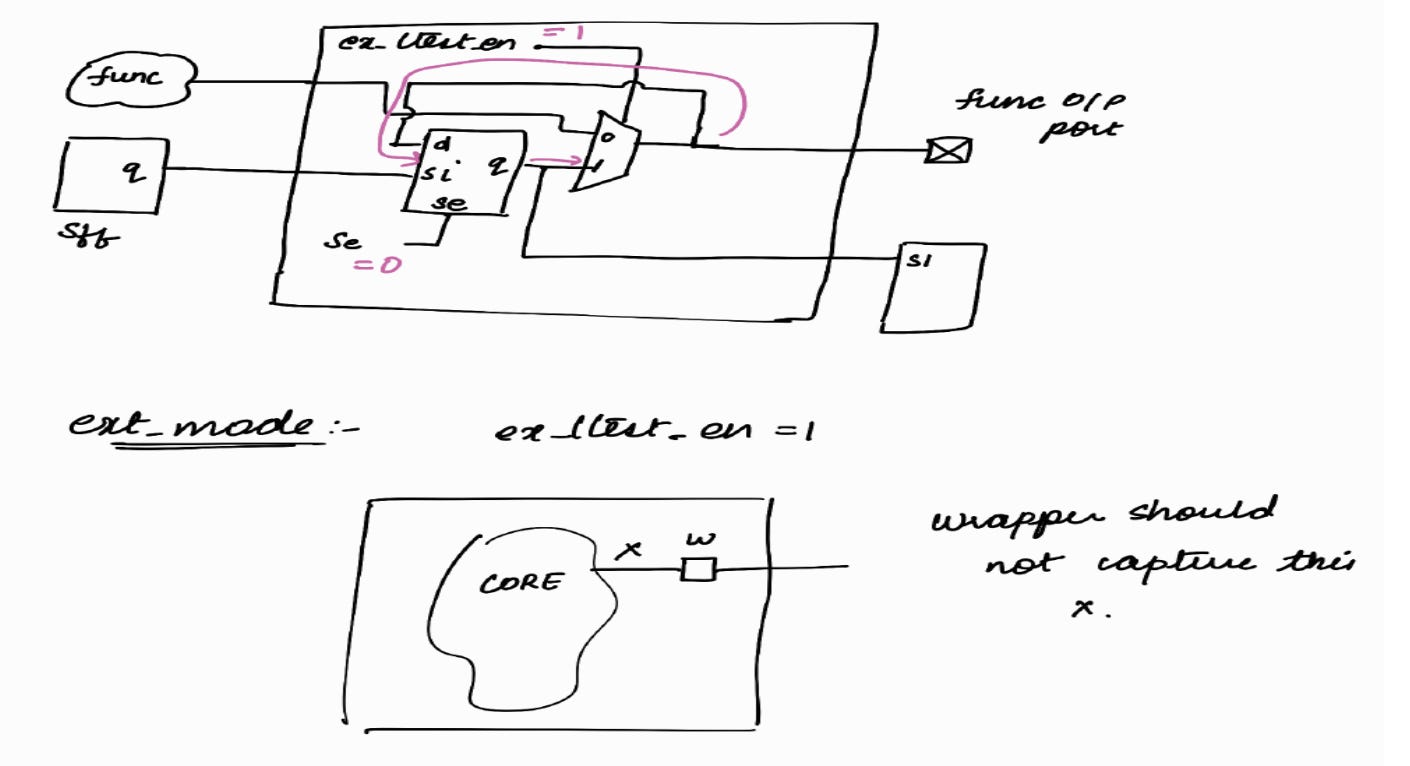
Capture Phase : (ext mode)
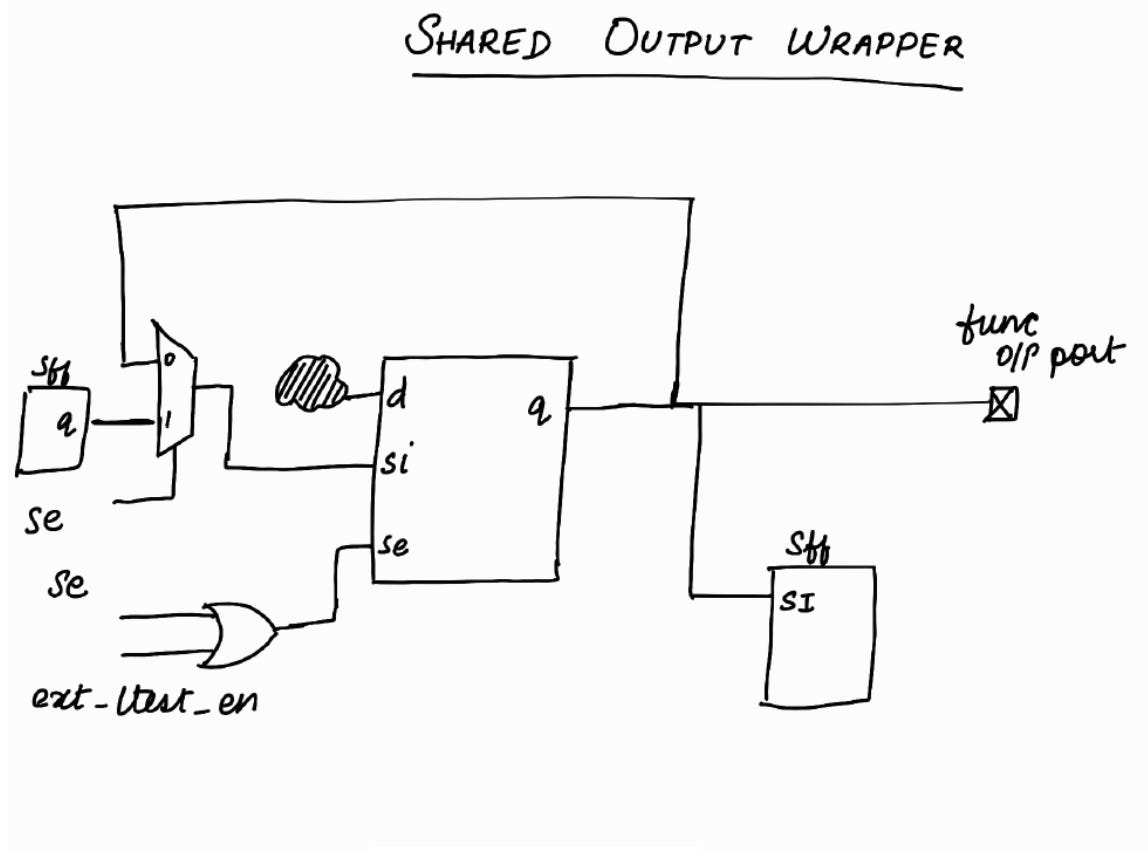
Let’s explore Shared Output Wrapper Cell !
Note :
se is Scan Enable. It will be a top level port.
ext_ltest_en will be controlled by TDR
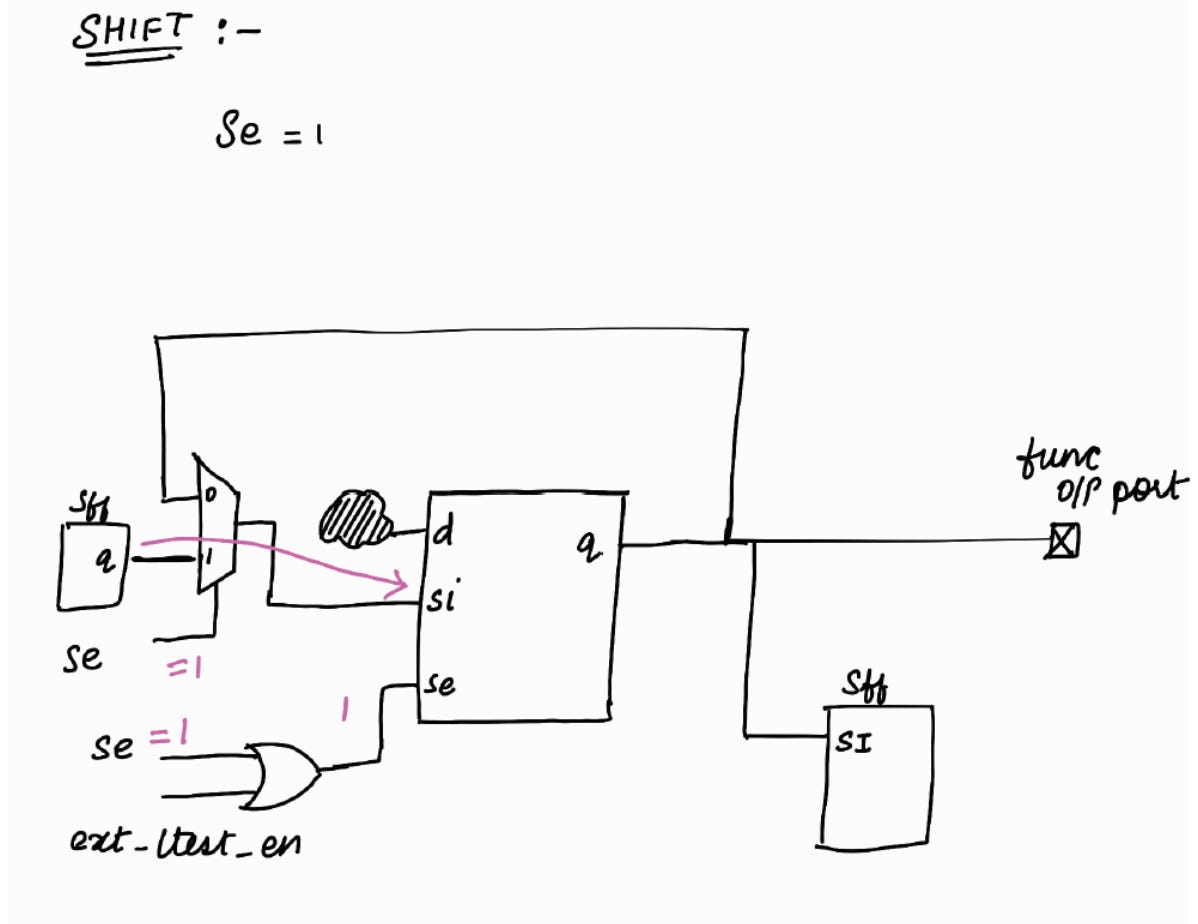
Shift Phase :
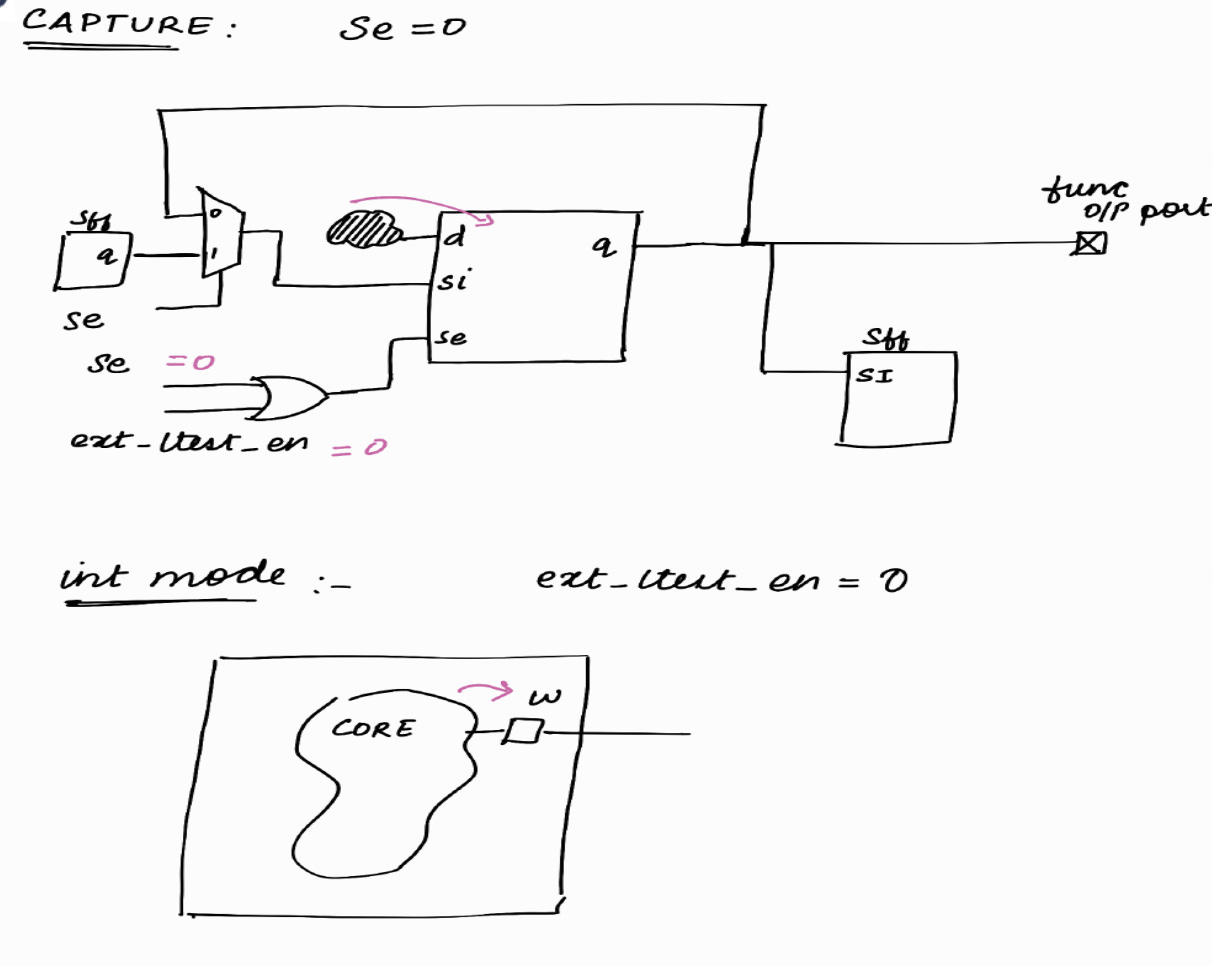
Capture Phase : (int mode)
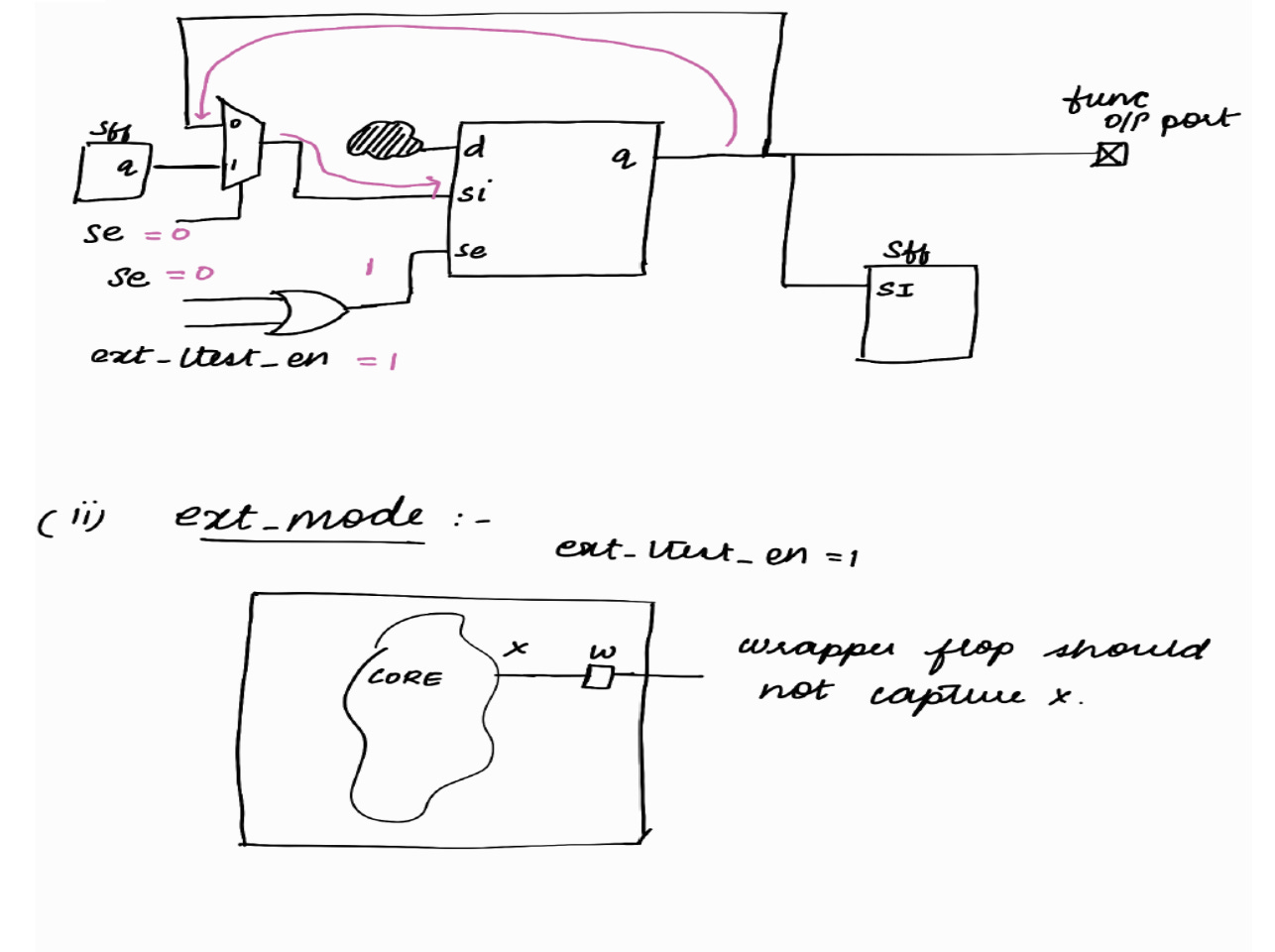
Capture Phase : (ext mode)
< < In ext_mode, the logic internal to the block will not be active. It will be X > >
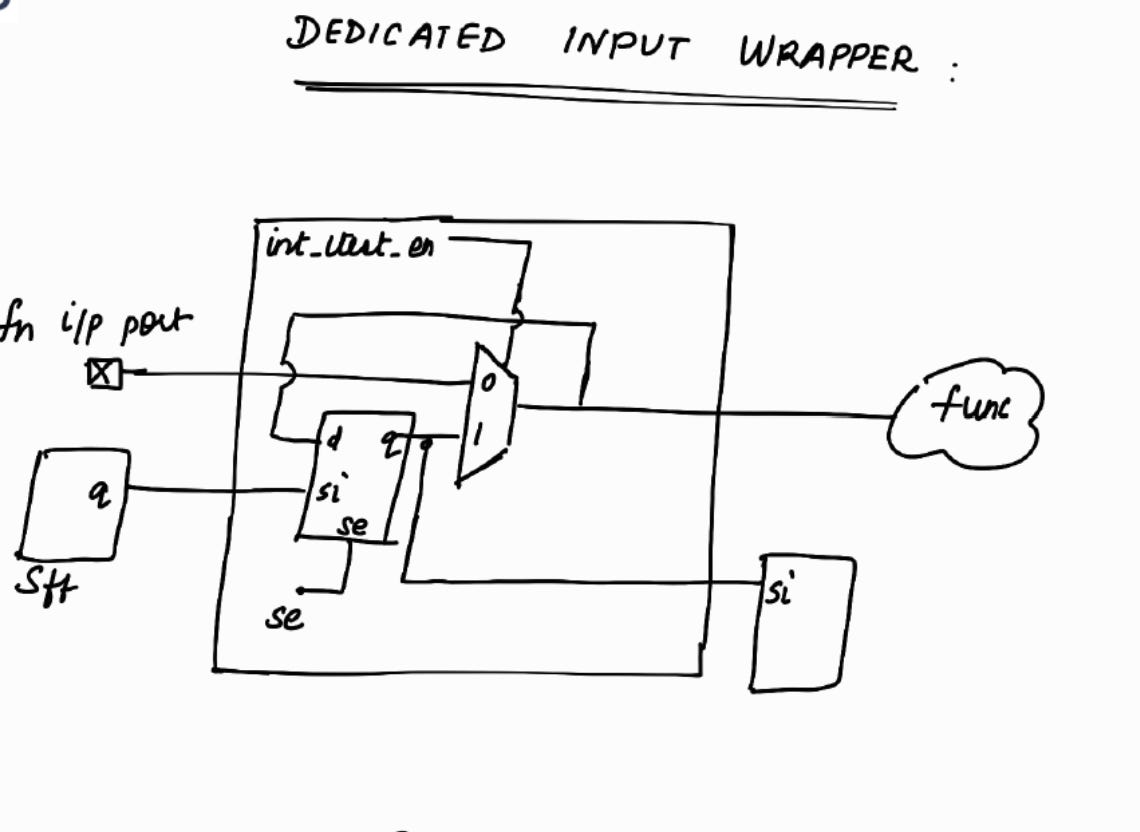
Let’s explore Dedicated Input Wrapper Cell !
Note :
se is Scan Enable. It will be a top level port.
int_ltest_en will be controlled by TDR
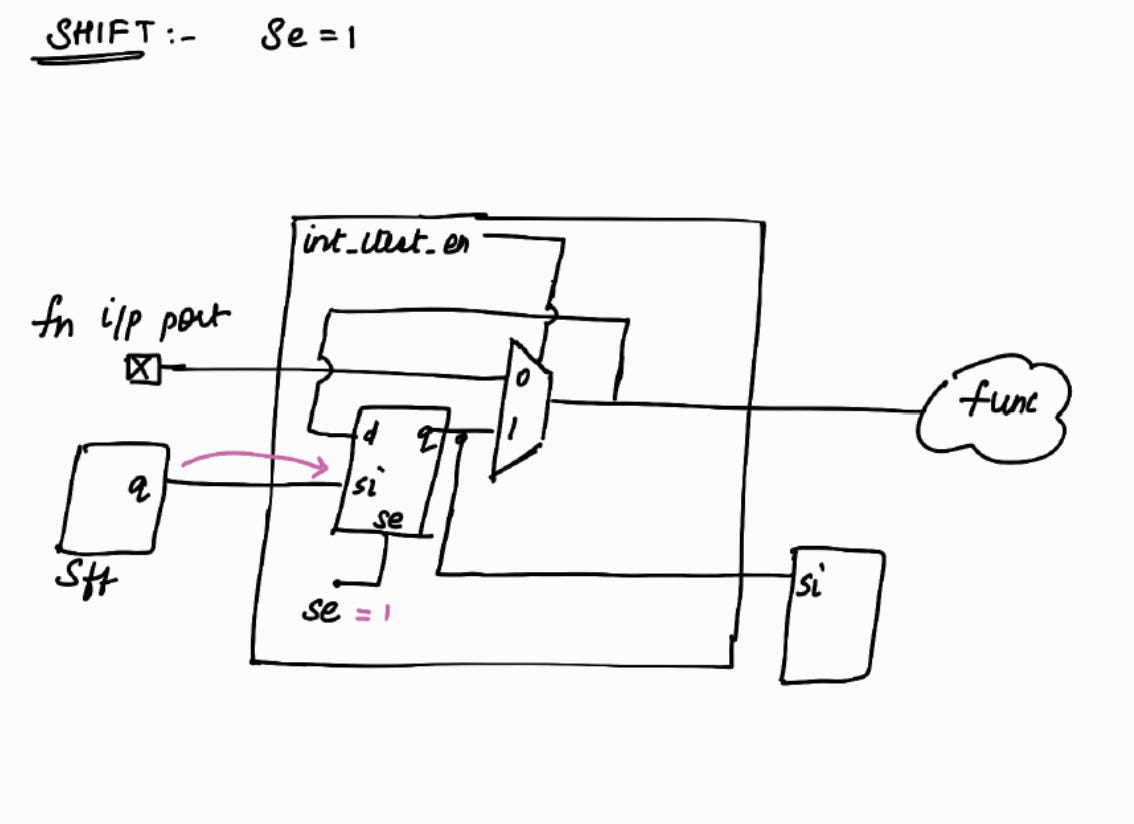
Shift Phase :
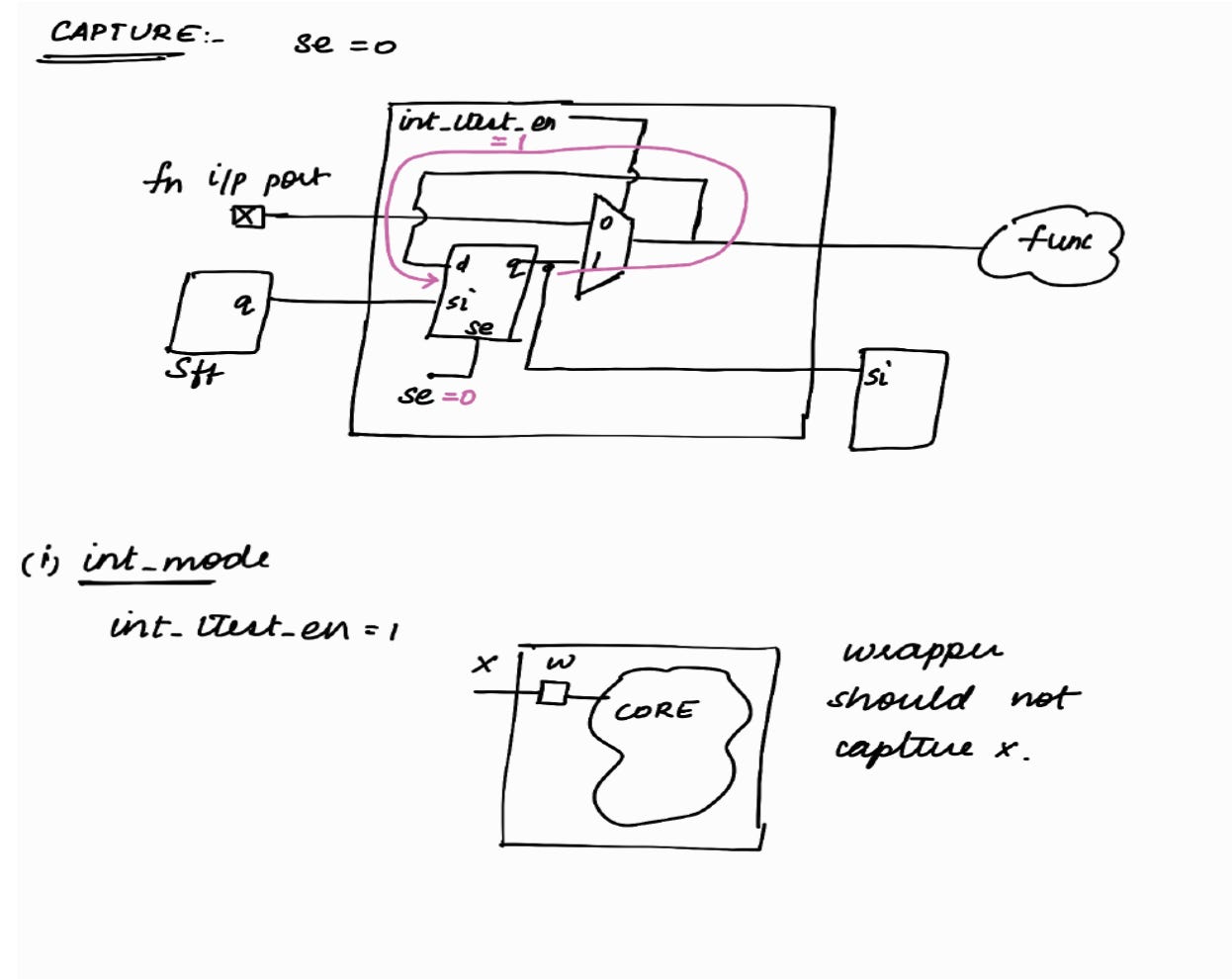
Capture Phase : (int_mode)
< < In int_mode, only the logic internal to the block will be active. Logic external to the block will not be active. It will be X > >
Capture Phase : (ext_mode)
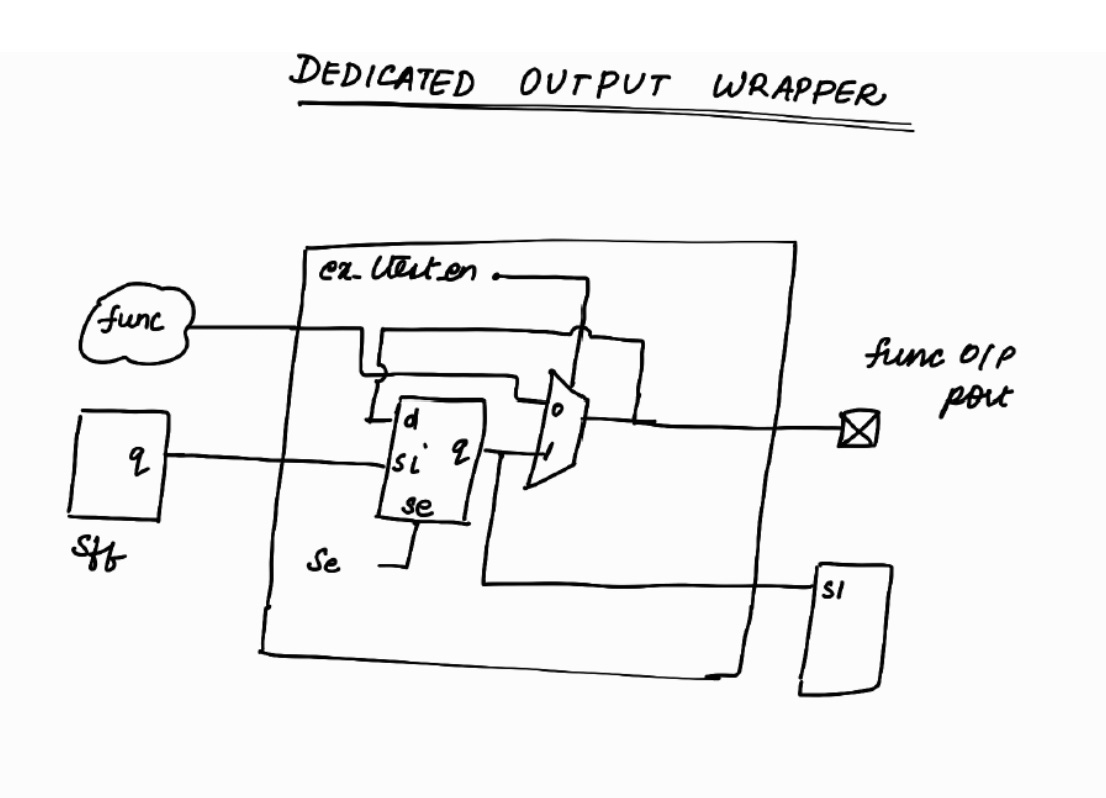
Let’s explore Dedicated Output Wrapper Cell !
Note :
se is Scan Enable. It will be a top level port.
ext_ltest_en will be controlled by TDR
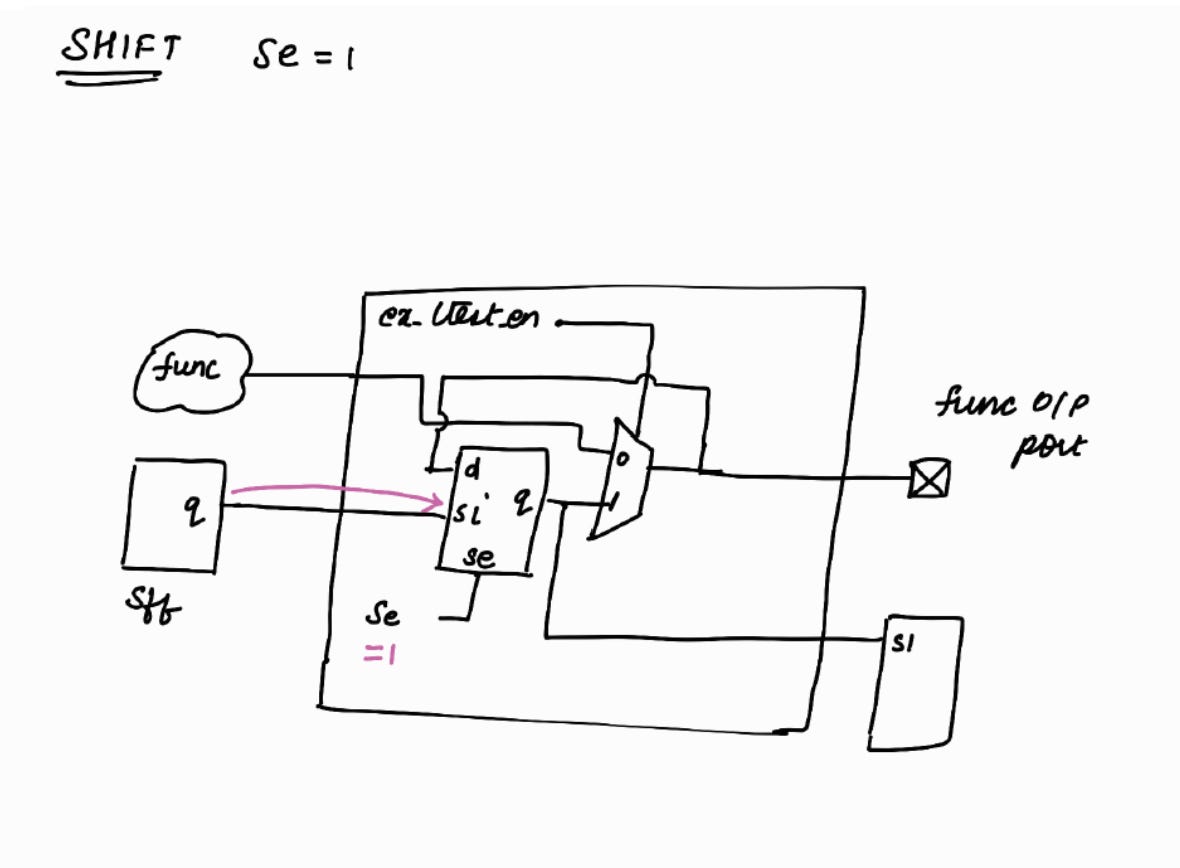
Shift Phase
Capture Phase : (int mode)
Capture Phase : (ext mode)
< < In ext_mode, the logic internal to the block will not be active. It will be X > >
Let’s summarize the points which we explored above
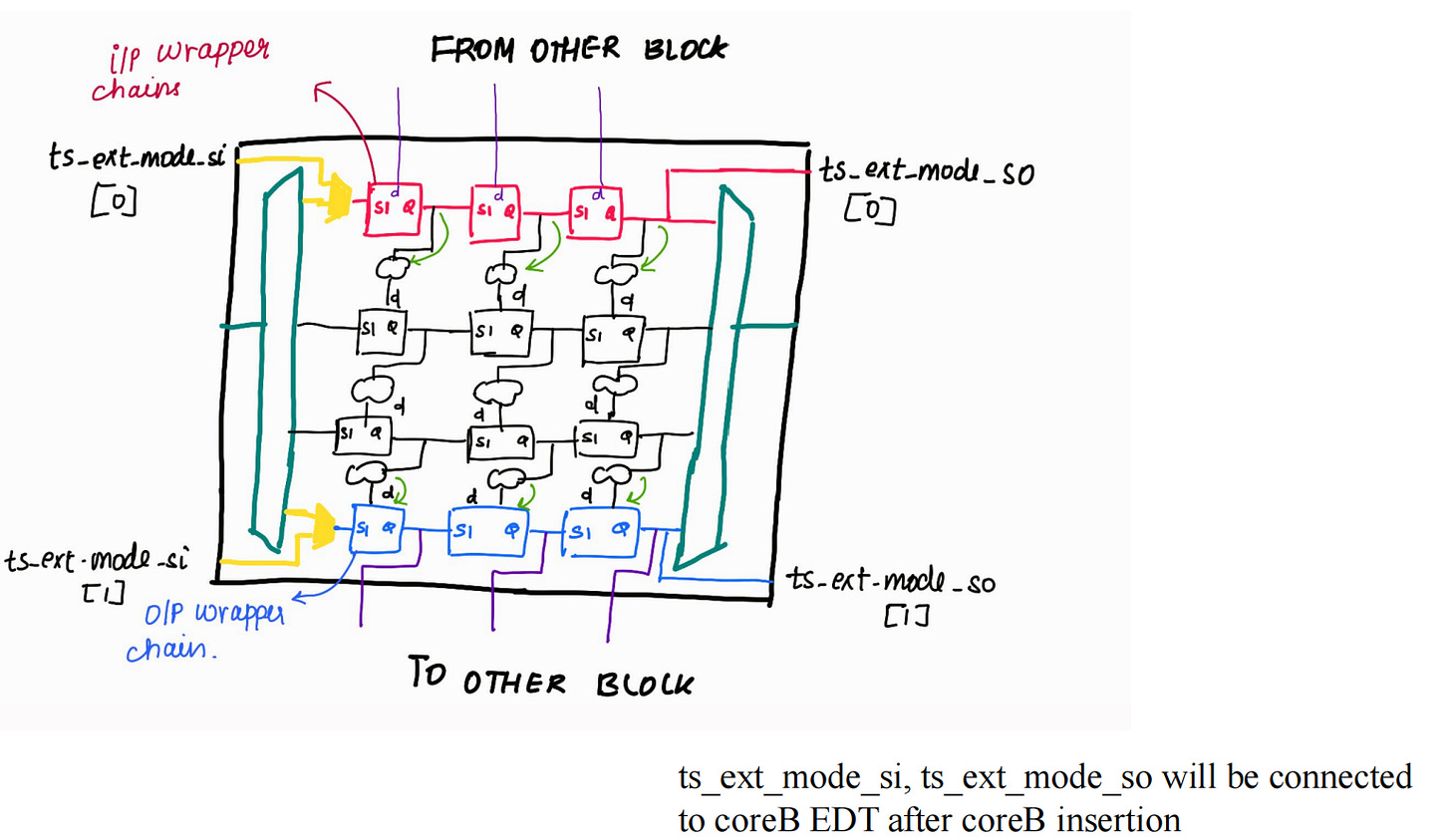
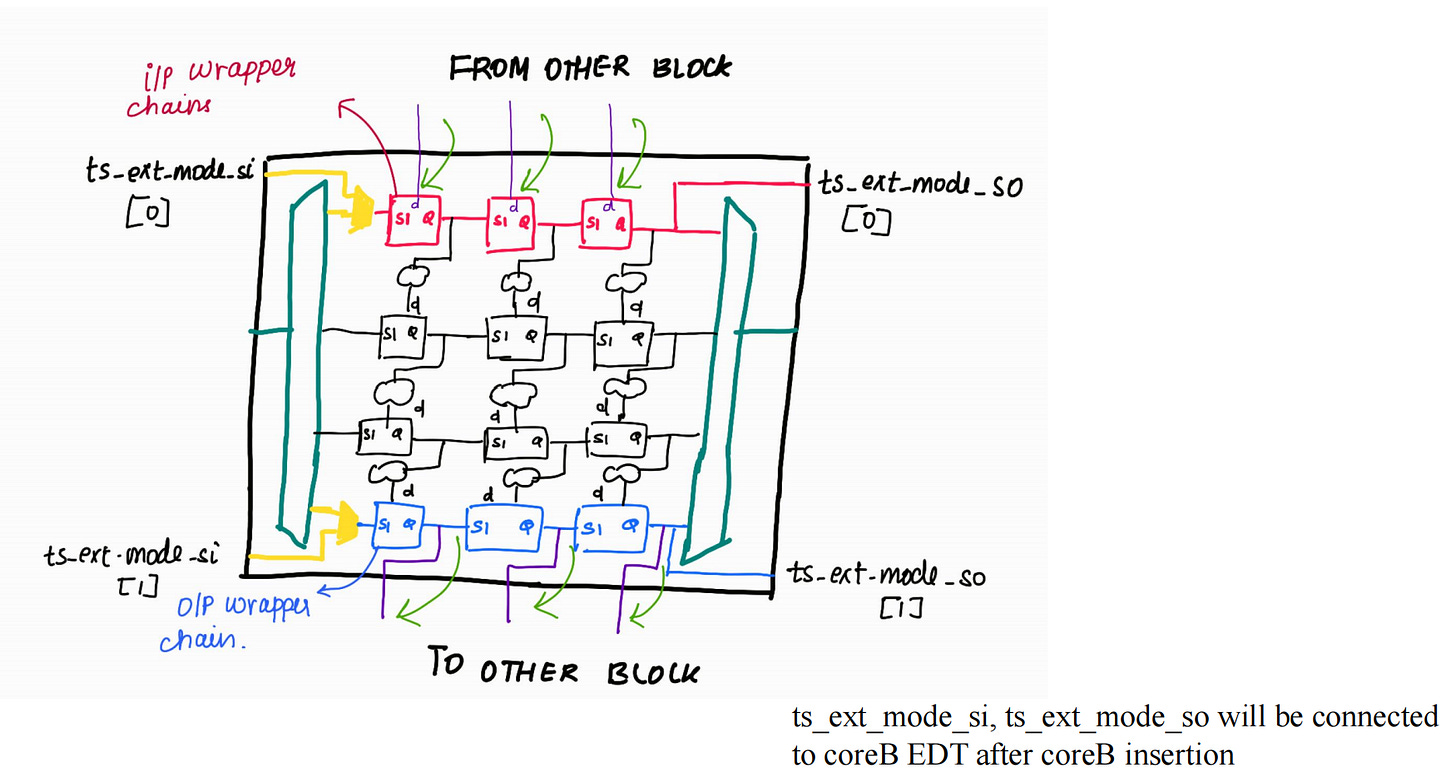
Wrapper Chains
References :
Tessent Scan and ATPG user’s manual
Wrapper Chains by Semicon shorts
Integrating Wrapped Cores in a Compressed Scan Flow - From Solvnet






Thank you for the detailed post!
A question on the wrapper cell:
There could be a XOR gate on the Q-D loopback for wrapper cell, to enable at-speed coverage.
Thanks for sharing this post.
I have some confusion about the function of the wrapper cell and boundary scan.
In the SoC hierarchical scan view, one of the benefits of the wrapper cell is to check the interconnection between block levels.
As I understand, boundary scan is used to check the interconnection at the board level.
So, boundary scan insertion is mainly done to enable board-level testing, right? I mean at the SoC level, it’s just prepared for board-level testing.